
What we covering
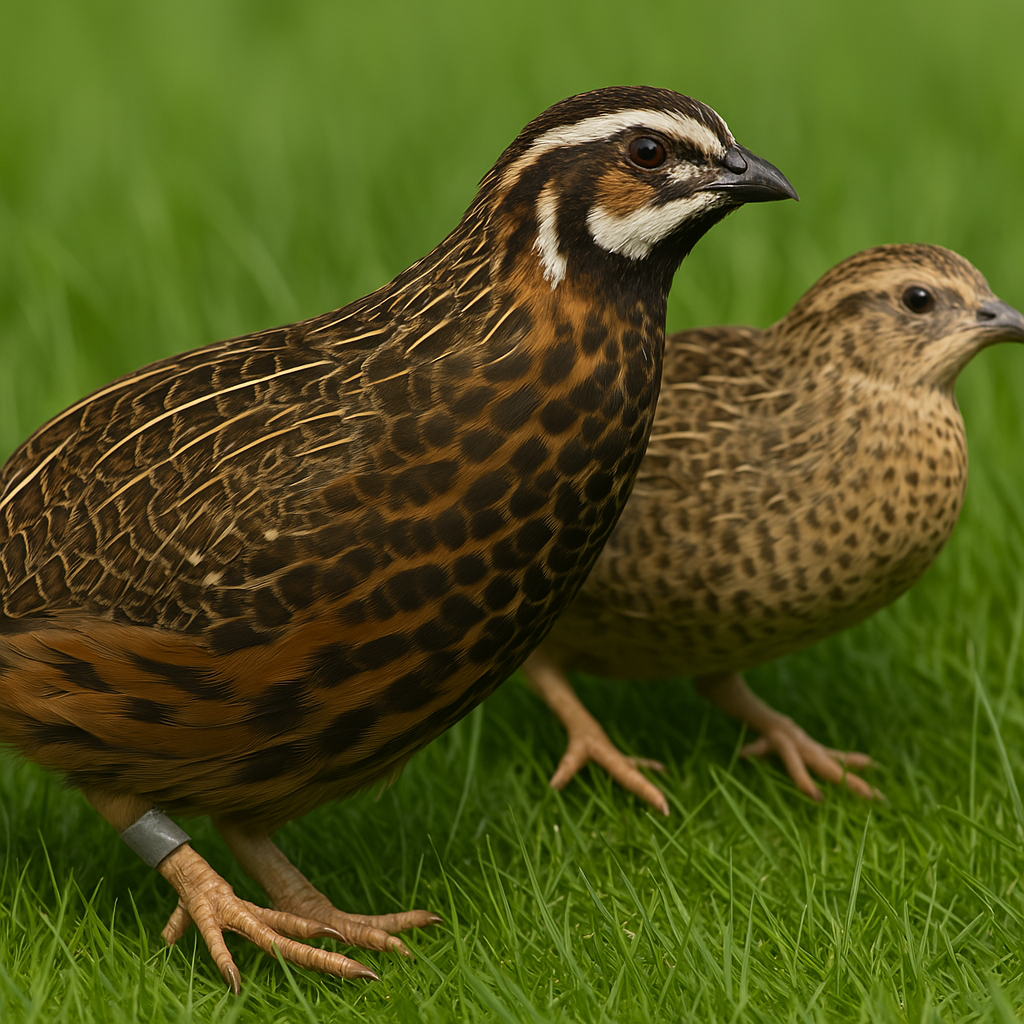
QuailMind provides detailed guidance on how to differentiate between male and female quails across various species. This includes visual markers such as feather coloration, size, and patterns. Males often display brighter or more pronounced plumage, particularly around the head and chest. In some species, such as Japanese quail, males may have a reddish breast, while females have more subdued, speckled feathers.
We have all you need to know about male and female quails
How To Vent Sex
Vent sexing is a reliable method for determining the sex of quail, especially in species where males and females have similar feather coloration. This technique involves examining the quail's cloaca (vent) for specific characteristics indicative of their sex.
How to feather sex. Read more hereFeather Sex
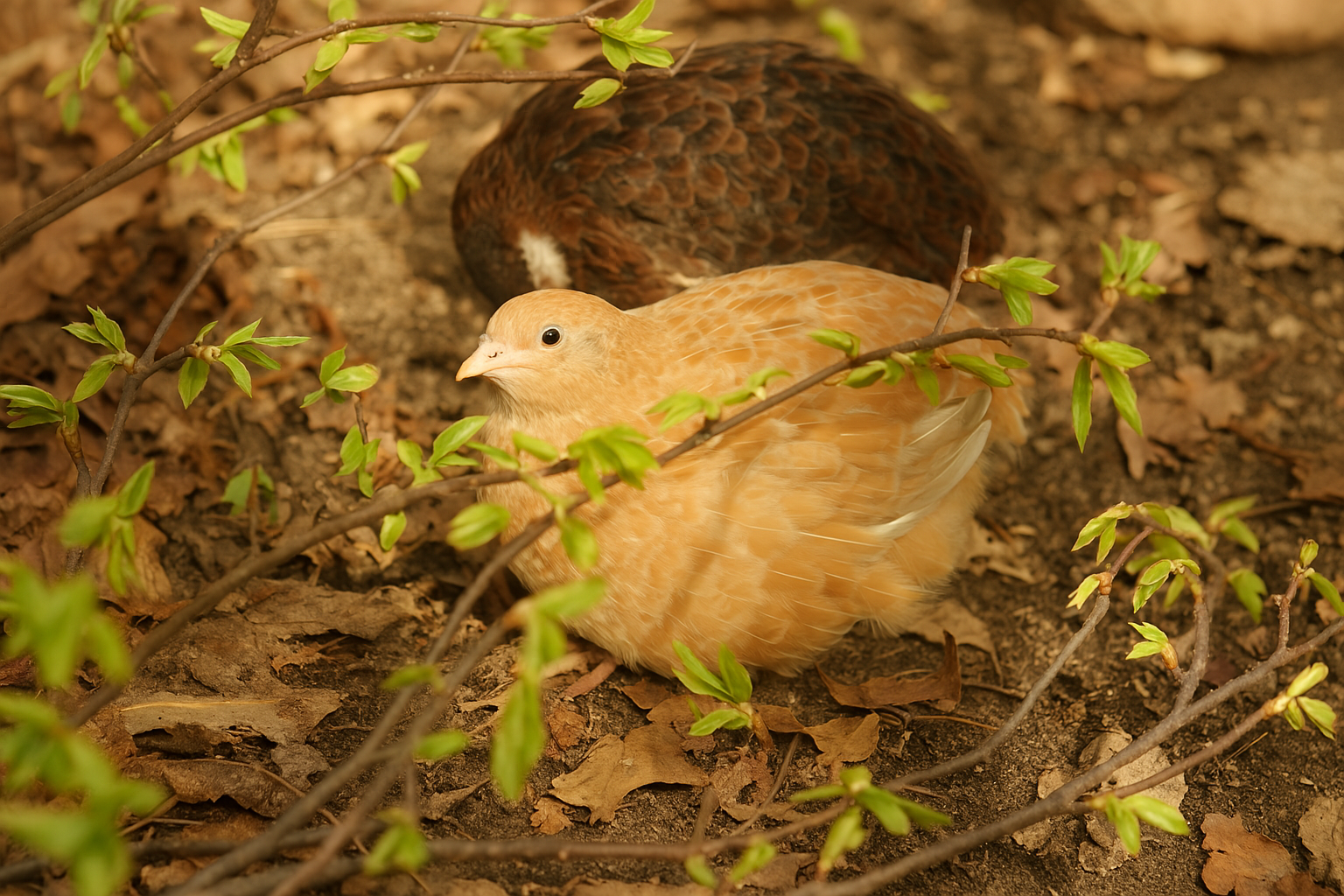
Feather sexing is a method used to determine the sex of quail chicks based on the characteristics of their feathers, particularly effective in certain color variations like Pharaoh and Italian quail.
How to vent sex. Read more here

Jumbo Celadon Quail
In Jumbo Celadon quail, the differences between males and females are relatively easy to spot, especially in adults. Females usually have speckled or mottled chests, while males have a smoother, more uniform chest color.
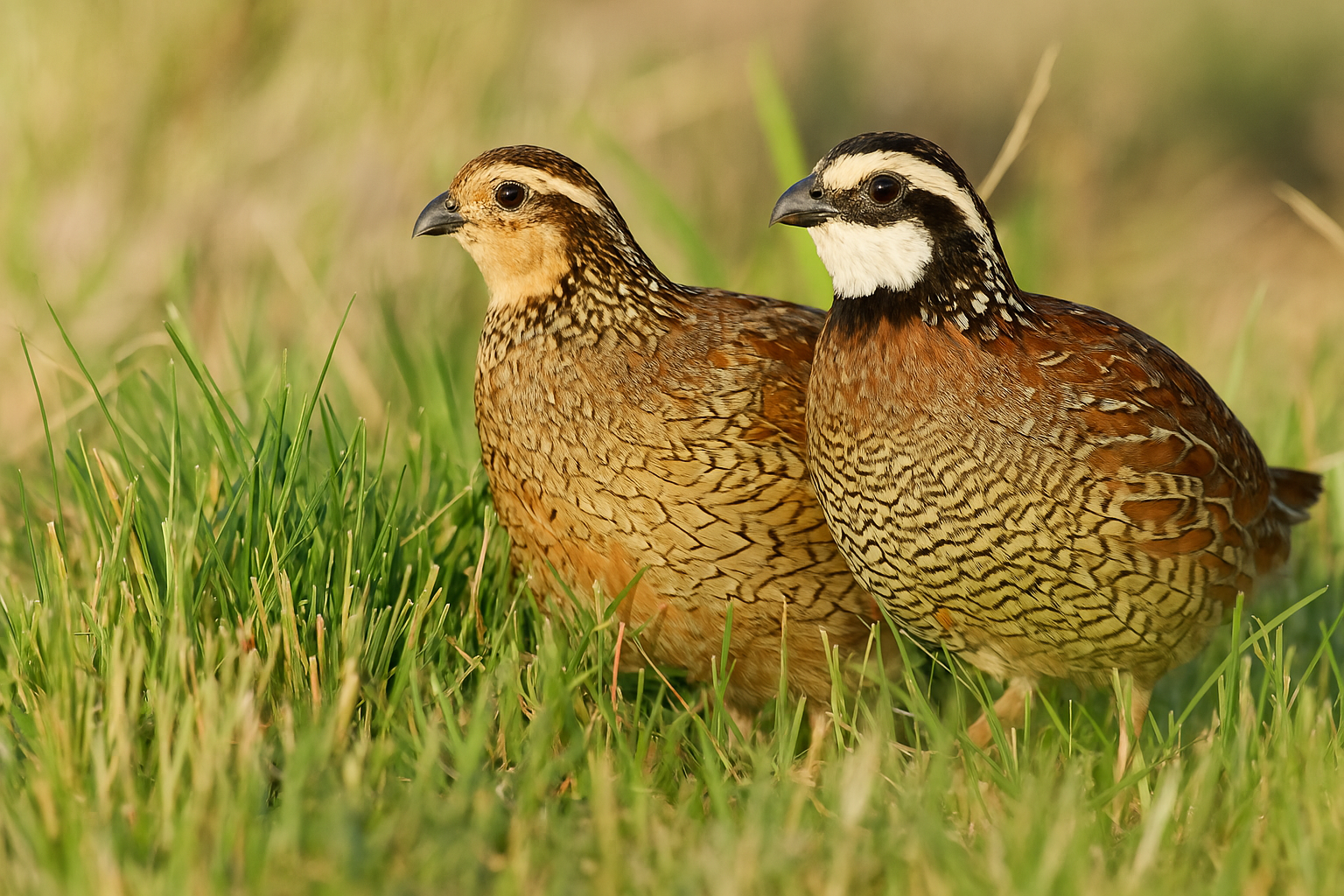

Bobwhite Quail
In bobwhite quail, males are distinguished by a white throat and a bold white stripe above their eyes, while females have a buff-colored throat and eye stripe, giving them a softer appearance. These differences are most apparent in adult birds. Sexing juveniles can be more challenging but becomes easier as they mature and develop their plumage.
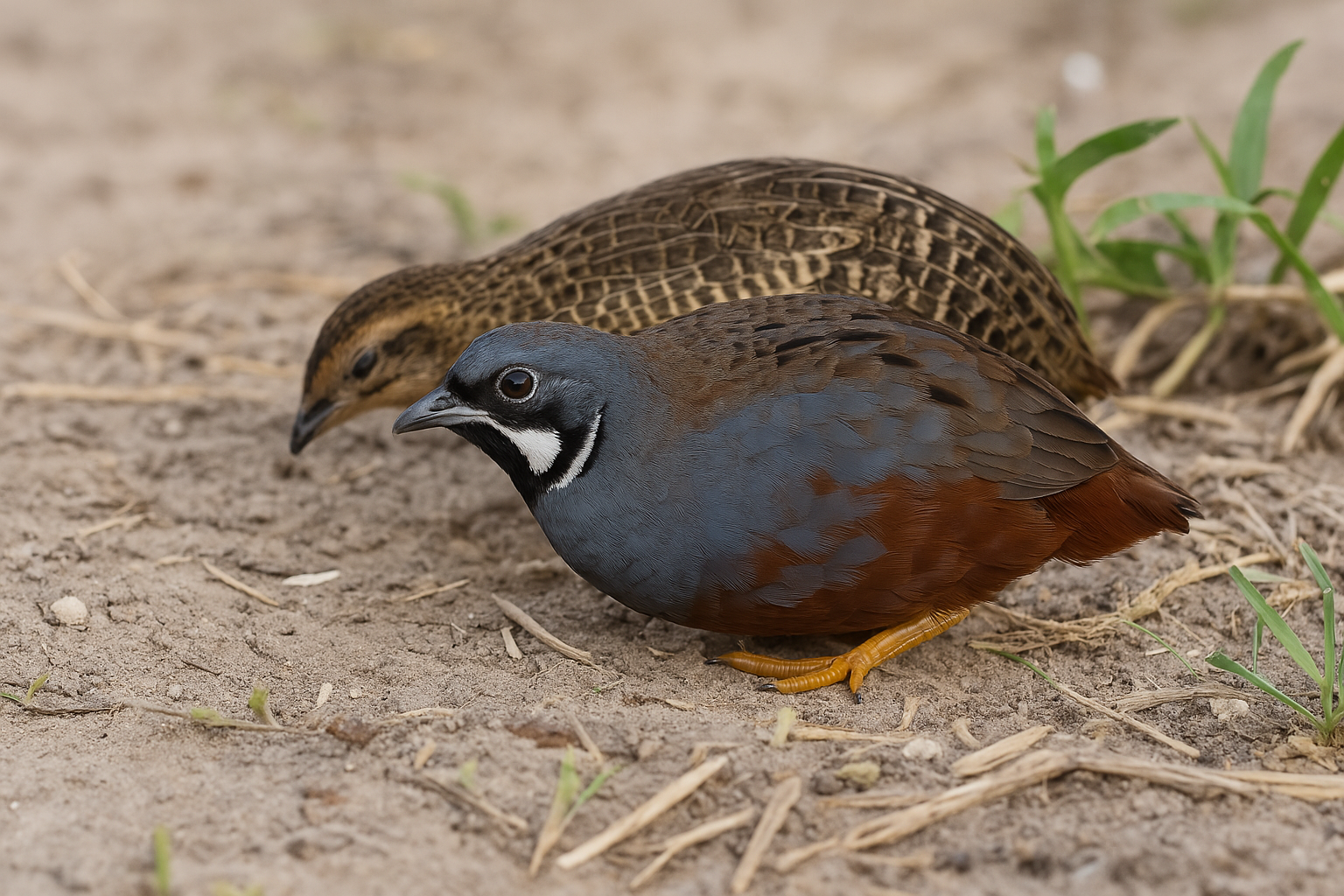

Button Quail
Male Chinese painted quail have bright chestnut throats and a white face outlined in black, while females are plain brown without bold markings. These differences make it easy to tell them apart in adults. Juveniles, however, may look similar until they mature.

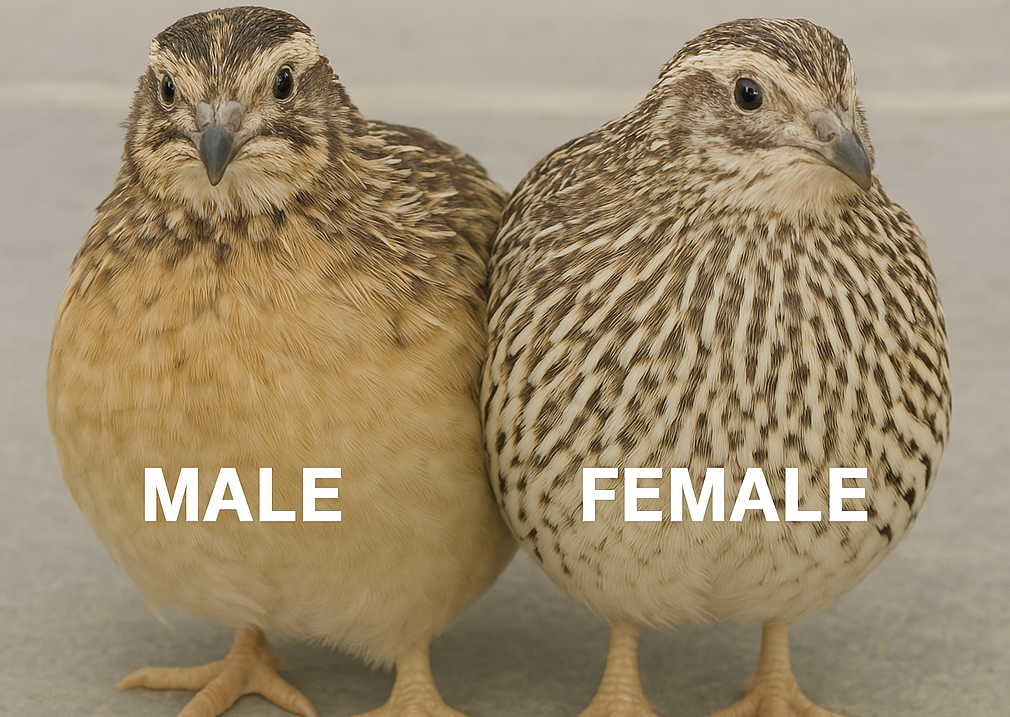
Coturnix Quail
(Japanese Quail)
In Coturnix (Japanese) quail, males and females have distinct differences in appearance. Males typically have a more vibrant plumage, with a rich chestnut color and a white throat patch, while females are generally more muted in color, with a dull brownish tone.
.png)
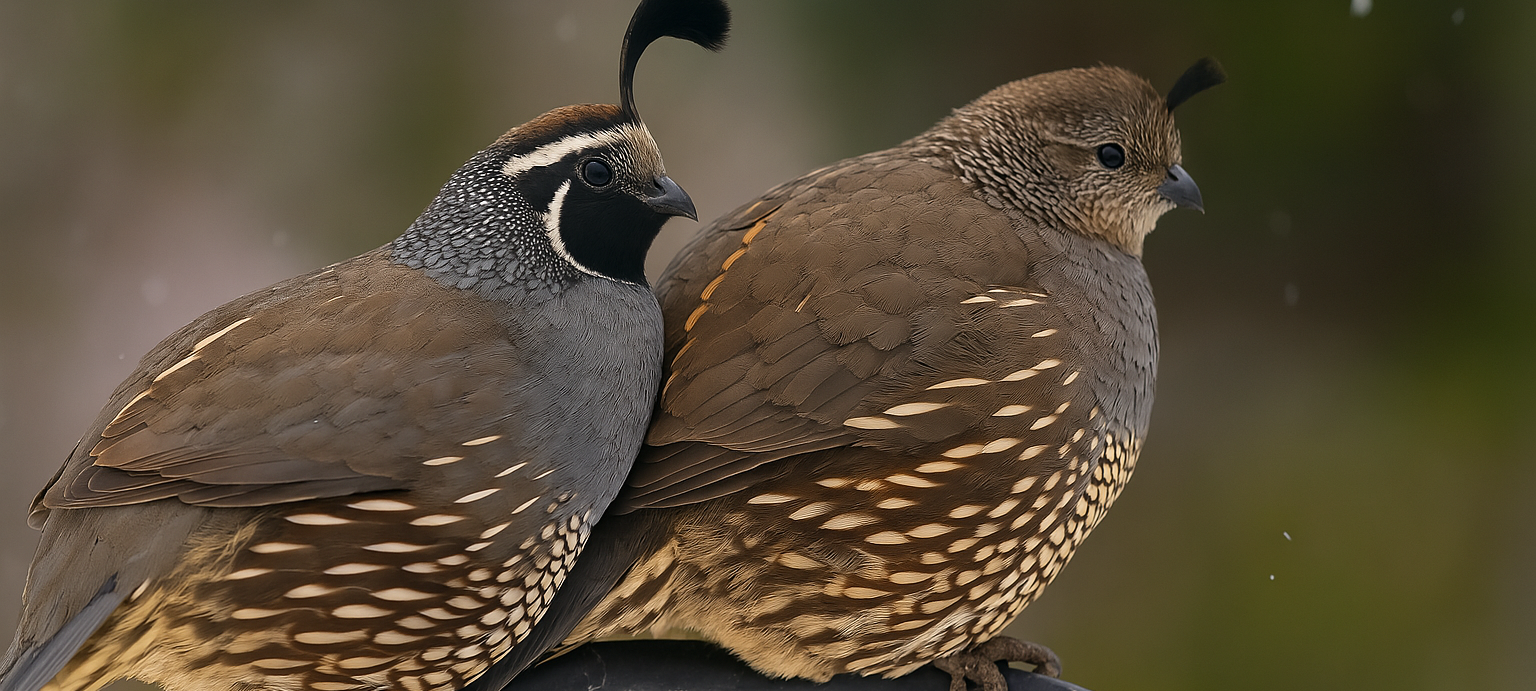
California Quail
Male California quail have a distinctive black throat and a larger, curved topknot, while females are more subdued in color with a brownish-gray chest and smaller topknot. These differences make it relatively easy to tell them apart.
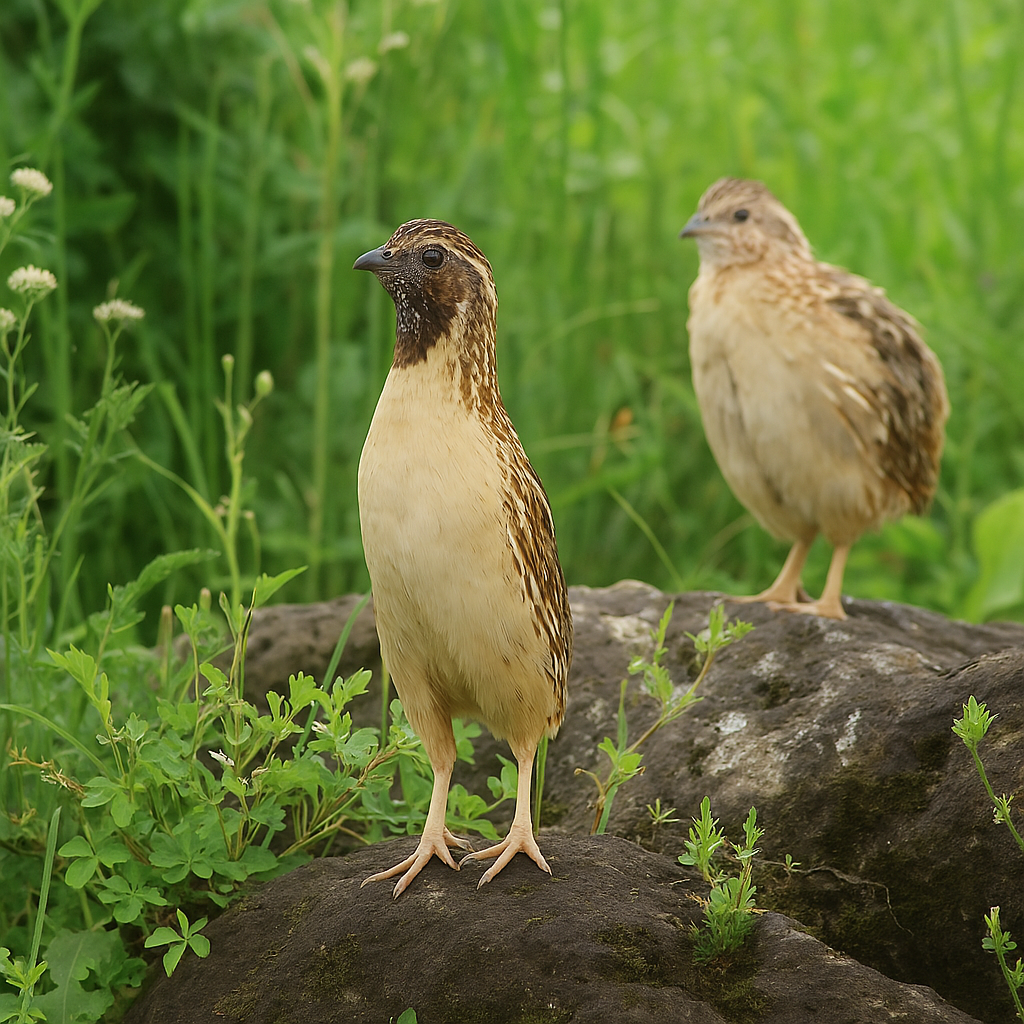

Common Quail
Males have brighter colors, especially a chestnut-colored throat and a dark facial line, while females are more muted in color. Males are also more vocal during breeding season. These traits make males easier to identify, though it can be harder outside of breeding time.
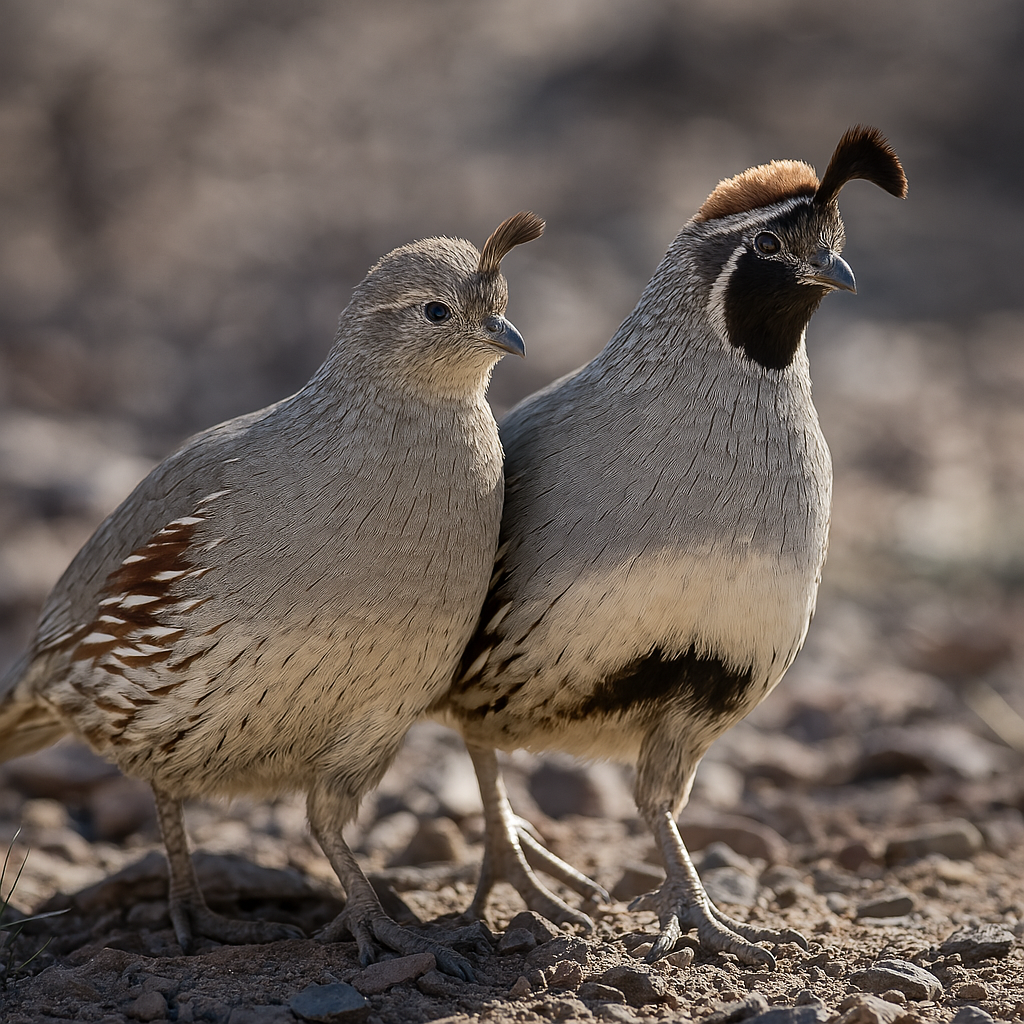

Gambel's Quail
Gambel's quail males and females are visually distinct, with males having a prominent black face mask, a white throat, and a curved topknot, while females are more subdued, and have a smaller topknot, and with a brownish head and less defined markings.
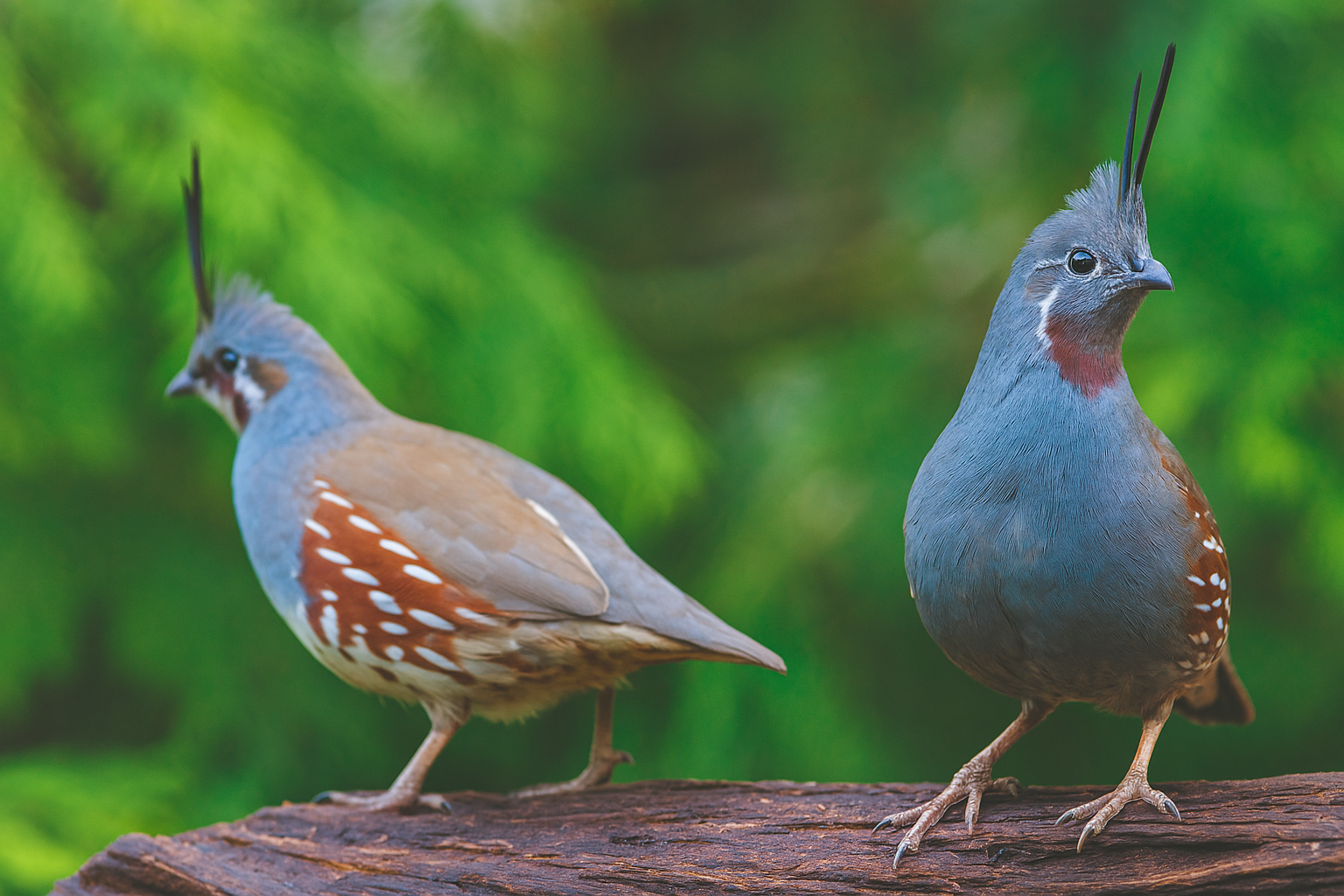

Mountain Quail
In mountain quail, males and females are similar in appearance, but males are typically slightly larger with more vibrant plumage. The male often has a more pronounced topknot and a slightly richer chestnut color on the breast, while females have a more muted, browner tone. The differences are subtle, making it difficult to visually distinguish them unless closely observed.
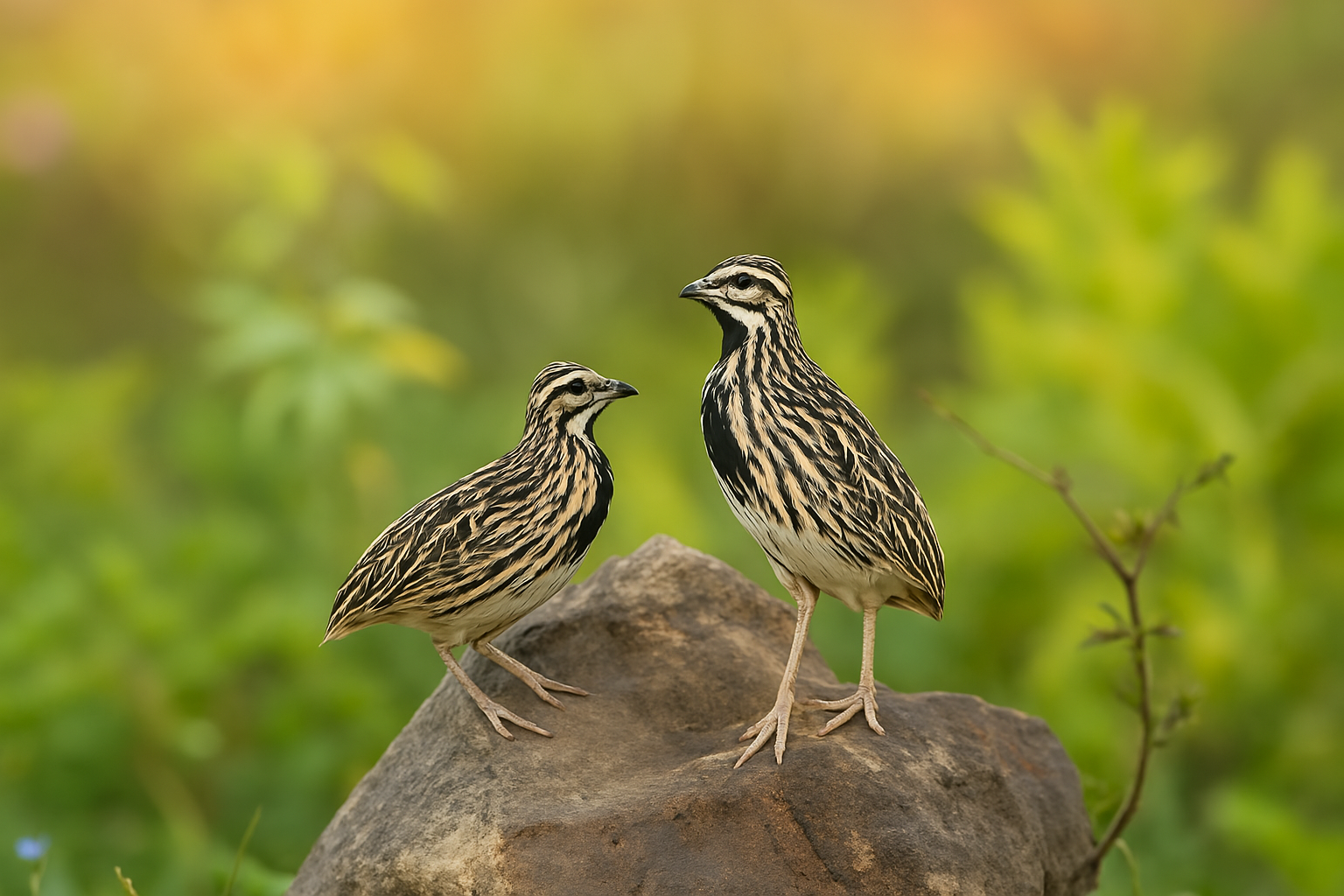

Rain Quail
In rain quails, males and females are quite similar in appearance, but there are subtle differences. Males typically have a slightly more vibrant coloration, with a brighter chest and sometimes a more distinct pattern on their feathers. However, these differences can be hard to spot without close observation. Females are generally more muted in tone, making it challenging to tell them apart, especially from a distance.

Harlequin Quail
Male harlequin quail are brightly colored, with a black throat patch and vivid chest markings. Females have more subdued brown and gray feathers, lacking the male's vibrant hues. This contrast in coloration makes it easy to tell them apart. The differences are especially noticeable in close observation.
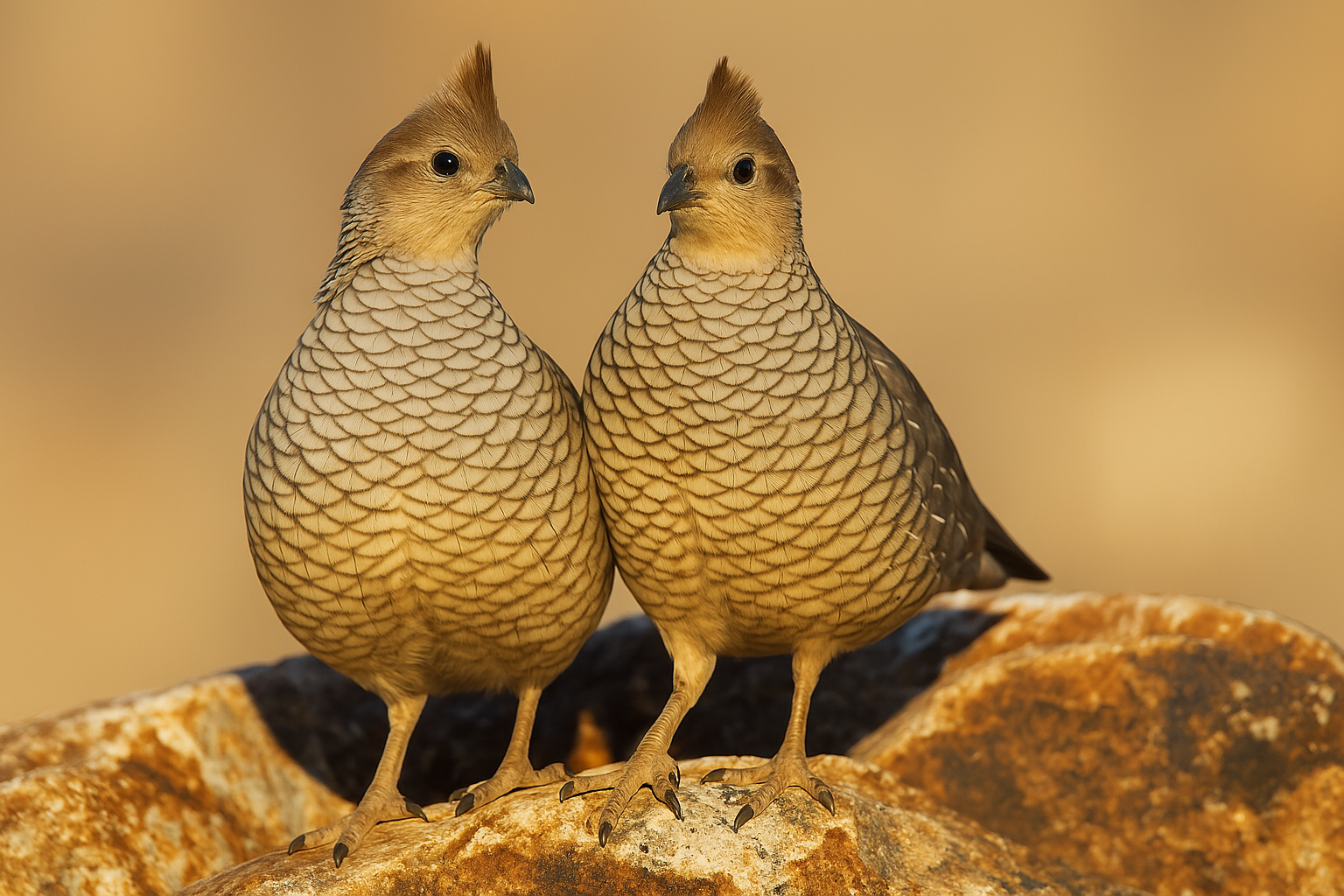

Scaled Quail
Scaled quail exhibit clear differences between males and females. Males have a more prominent crest on their head, a darker, richer coloration with a more defined scaled pattern, and a black throat patch. Females tend to be slightly more muted in color, with a less noticeable crest and a more subtle scaled appearance. These differences are typically easy to spot, especially in mature birds.
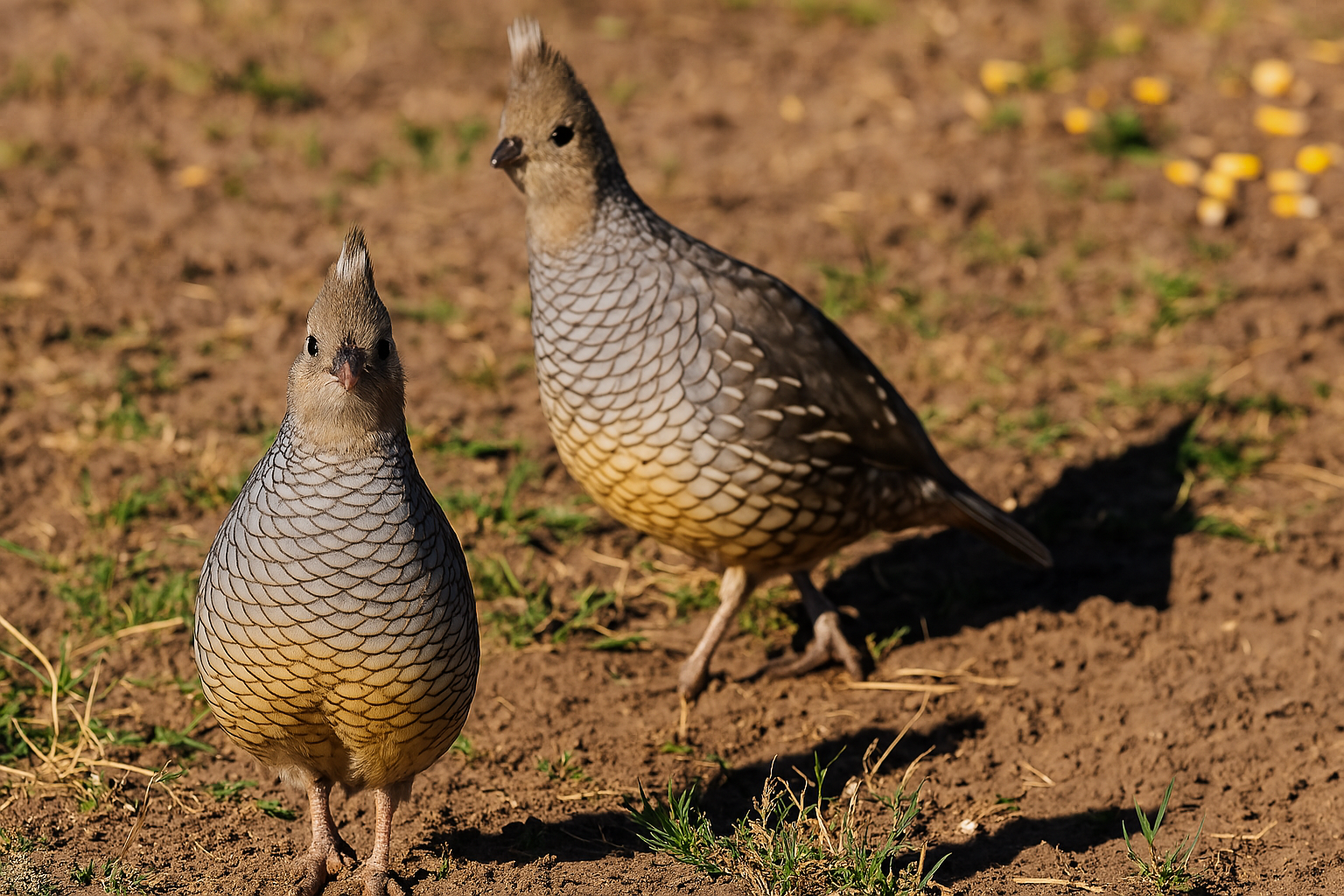

Texas Blue Scaled Quail
The Texas blue-scaled quail exhibits sexual dimorphism, with males having vibrant blue-gray plumage and a bold white throat patch, while females are more muted and brownish. Males are easier to spot due to their striking blue colors, though both sexes blend well into their rocky, scrubby habitat.
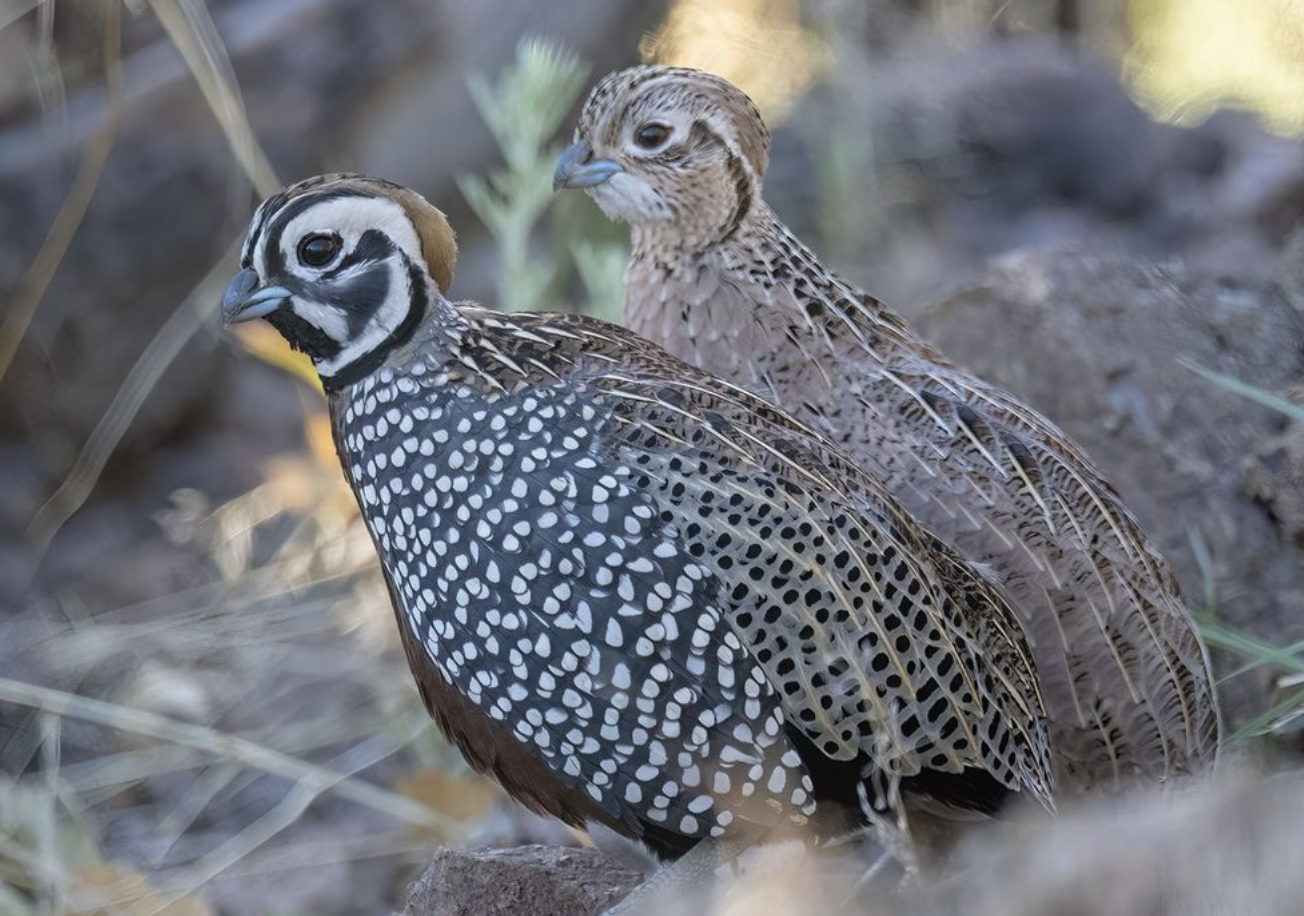

Montezuma Quail
Males display a striking, swirling black-and-white face pattern with a prominent tan crest, while females have a more subdued brown and buff coloration with only hints of facial markings. These differences in plumage and facial patterns help in identifying the sexes.