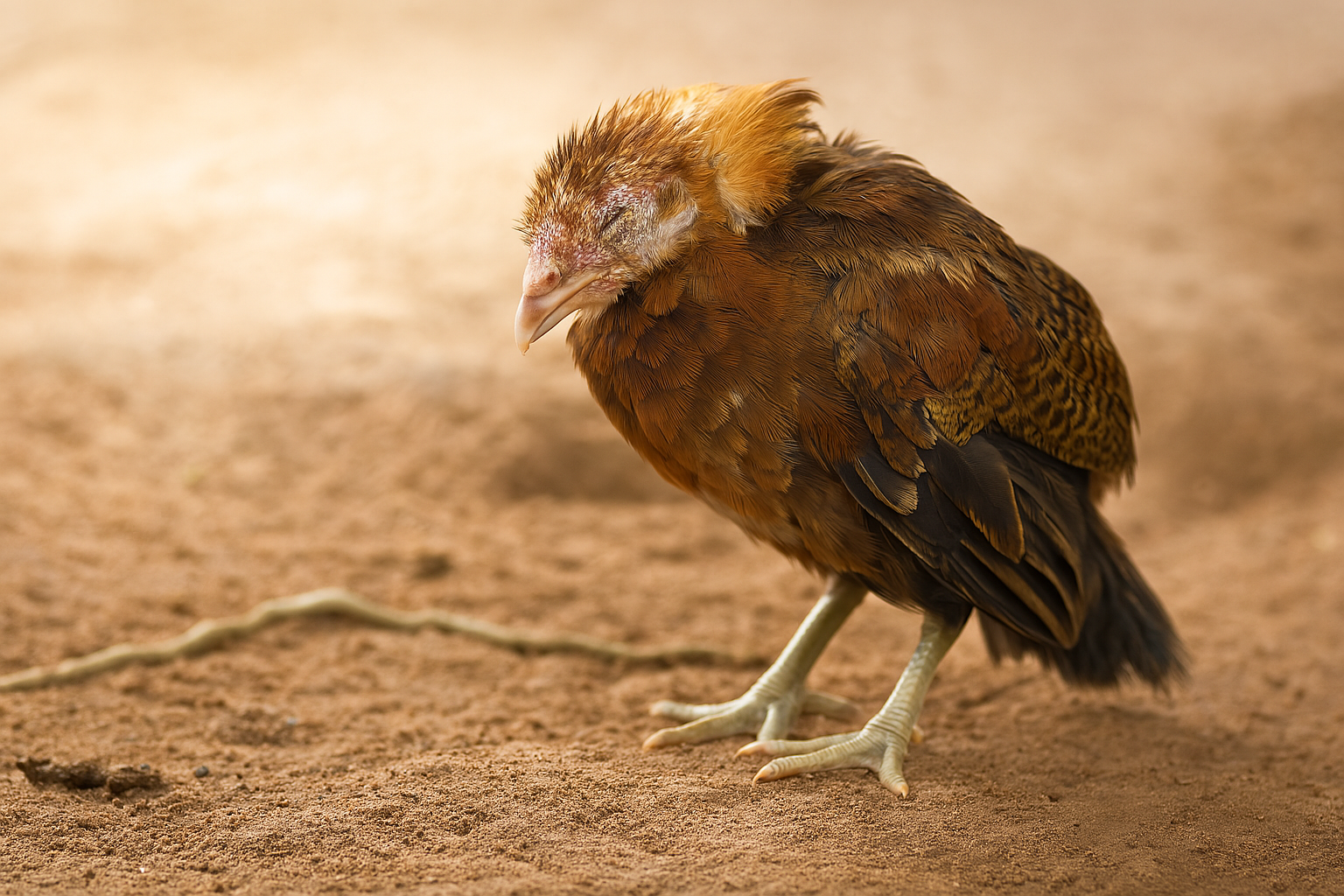


Coccidiosis
Coccidiosis is a common parasitic disease in quails caused by protozoa. It affects their digestive system, leading to symptoms like diarrhea, weight loss, and lethargy. In severe cases, it can result in dehydration and death if left untreated.
Read more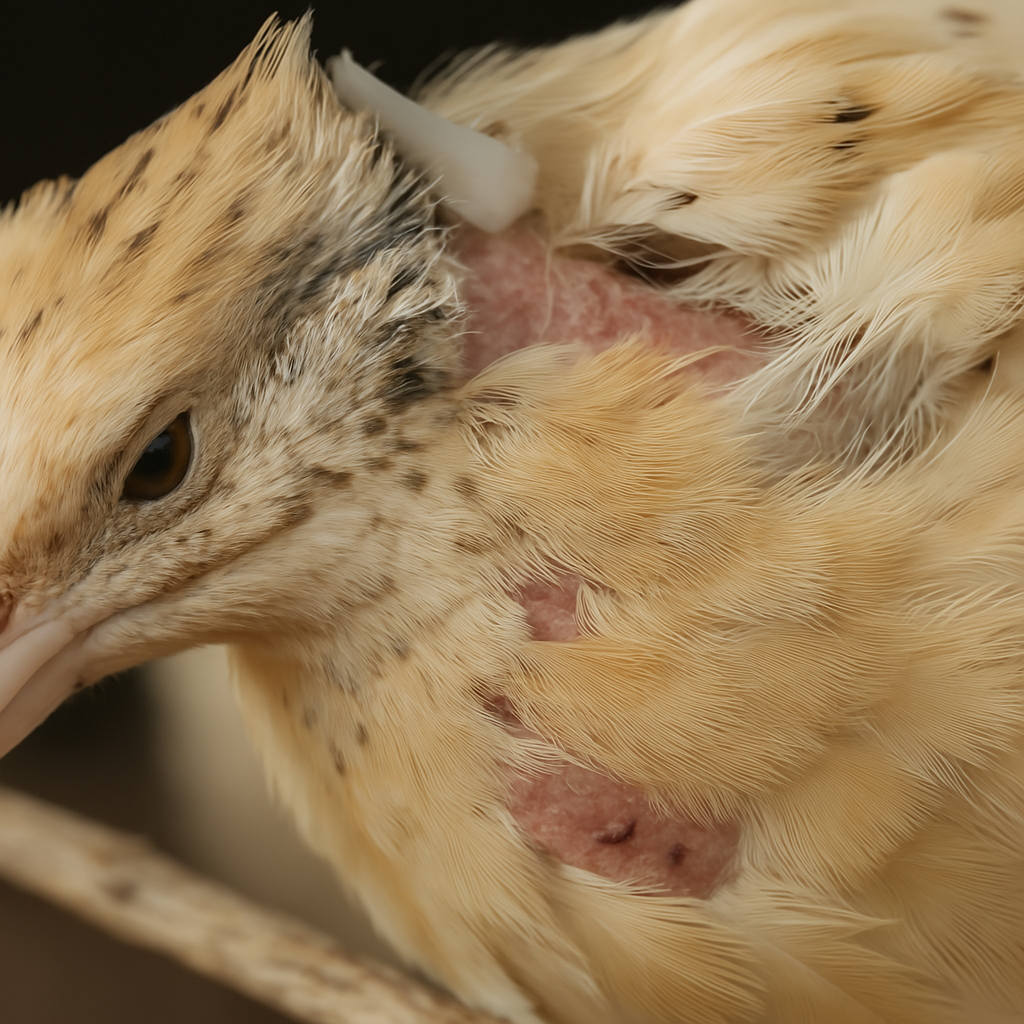
Mites and Lice
Mites and lice are common external parasites in quails. These pests irritate the birds by feeding on their blood, feathers, and skin. Signs of infestation include feather loss, excessive preening, restlessness, and reduced egg production. Mites hide in the quail's environment, while lice live directly on the bird. Regular cleaning, dust baths, and anti-parasitic treatments can help control infestations.
Read more
Splay Leg
Leg splay, also known as spraddle leg, is a condition in quail
where a chick's legs splay outward, hindering its ability to
stand or walk properly. This issue often arises from factors
such as slippery brooder surfaces, improper incubation
conditions, or nutritional deficiencies.
Read more
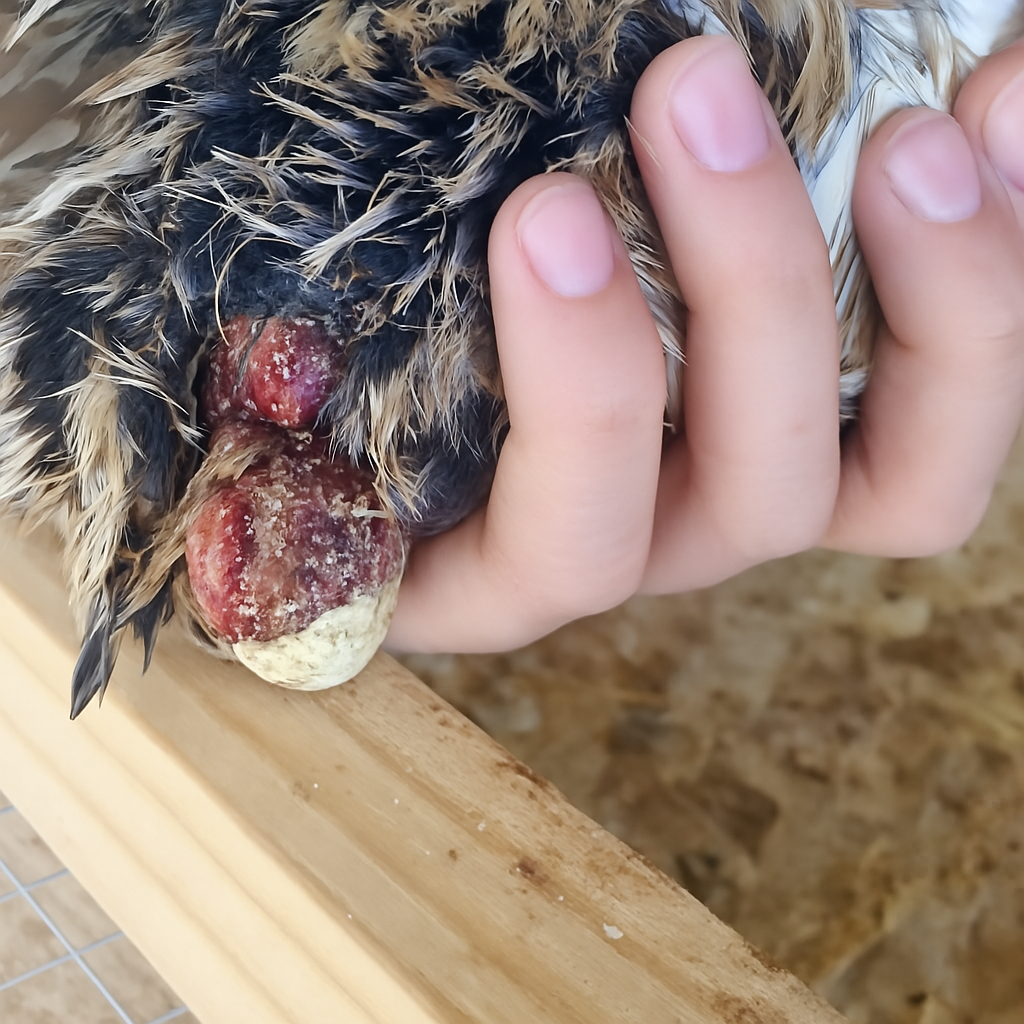
Egg Binding
Egg binding occurs when a female quail is unable to pass an egg. It can be caused by factors such as poor nutrition, lack of calcium, or oversized eggs. Symptoms include lethargy, straining, and swelling near the vent. Immediate veterinary care is often needed to assist with egg passage and prevent complications. Egg binding can lead to potential complications such as infection, internal damage, or even death.
Read more

Respiratory Infections
Respiratory infections in quails can be caused by various pathogens, including bacteria and viruses. Symptoms may include nasal discharge, coughing, and difficulty breathing.
Necrotic Enteritis
Necrotic enteritis is a bacterial infection caused by Clostridium perfringens. It affects the intestines, leading to severe inflammation, diarrhea, weight loss, and in some cases, sudden death. Proper hygiene, balanced diets, and clean water can help prevent outbreaks.

Botulism
Botulism in quails is caused by the toxins produced by Clostridium botulinum bacteria, often from spoiled or contaminated food and water. This can result in paralysis, weakness, and respiratory failure. Proper hygiene, clean water, and fresh feed are key to prevention.
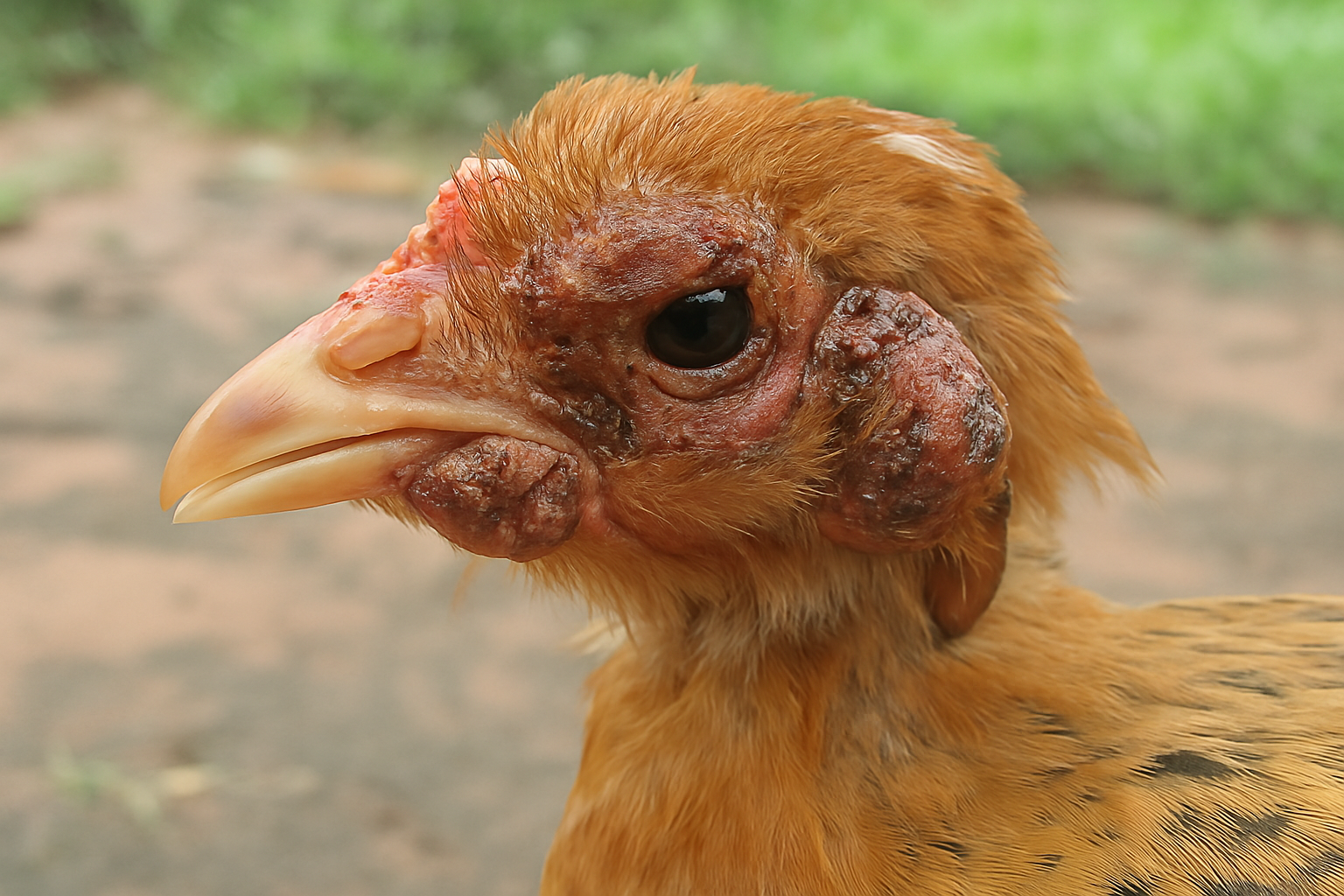

Fowl Pox
Fowl Pox is a viral disease in quails caused by the avian pox virus, leading to skin lesions and lethargy. It spreads through direct contact and contaminated surfaces. Vaccination and good hygiene practices are crucial for prevention, as the disease can cause secondary infections but is usually not fatal.

Avian Influenza
Avian Influenza, commonly known as bird flu, is a viral infection that can affect quails and other bird species. Symptoms include respiratory distress, lethargy, and decreased egg production. The virus can spread rapidly among birds, especially in crowded conditions. Preventive measures, such as biosecurity practices and vaccination, are essential to control outbreaks and protect flock health.

Chlamydiosis
Chlamydiosis in quails is caused by the bacterium Chlamydia psittaci, leading to respiratory symptoms, lethargy, and decreased egg production. Infected birds may exhibit nasal discharge, conjunctivitis, and signs of distress. It's primarily spread through direct contact with infected birds or contaminated environments. Proper hygiene, isolation of sick birds, and veterinary care are essential for prevention and management.
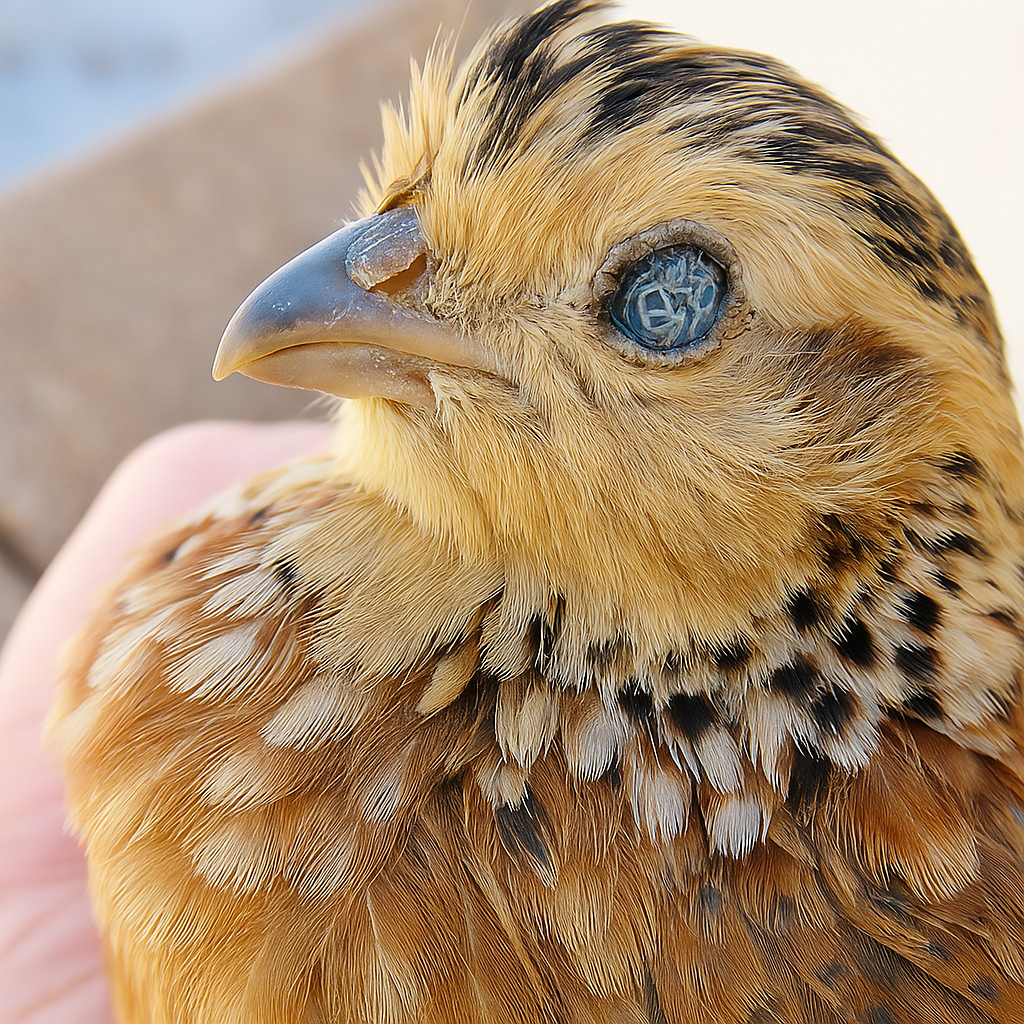

Internal Parasites
Internal parasites in quails, such as roundworms and flatworms, can cause various health issues. Infected birds may show signs of weight loss, diarrhea, and lethargy. These parasites can affect the digestive system, leading to poor nutrient absorption and overall weakness.